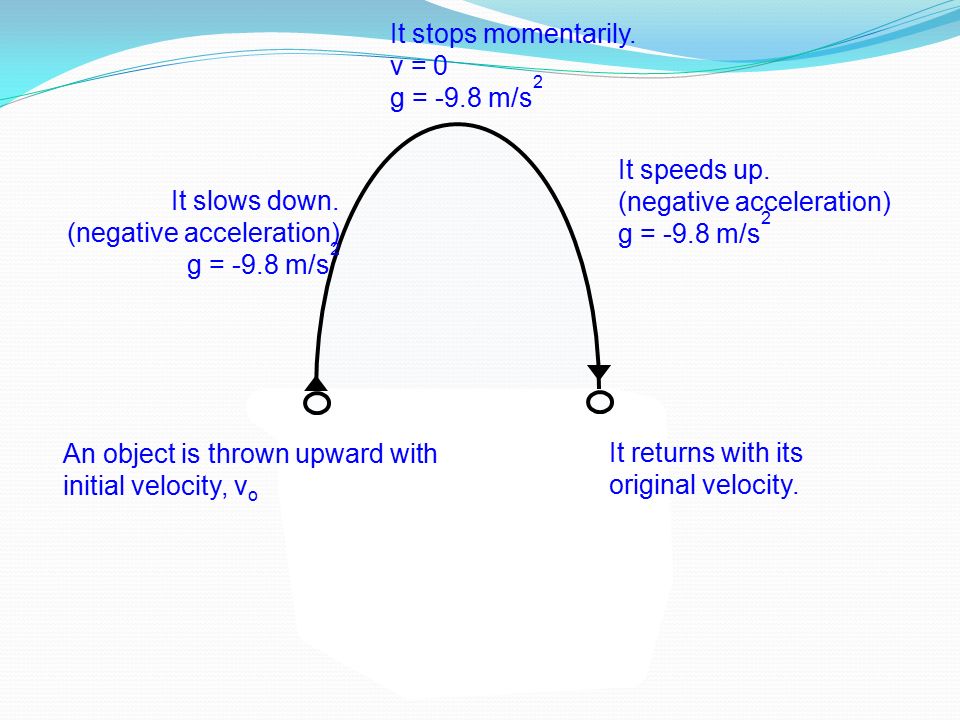
Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration . the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. newton's first law can be used to explain the movement of objects travelling with uniform motion (constant velocity). if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. For example, a particle with. if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec.
from socratic.org
the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec. if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. newton's first law can be used to explain the movement of objects travelling with uniform motion (constant velocity). to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. For example, a particle with.
When is it possible for velocity to be zero for an object that would be
Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. newton's first law can be used to explain the movement of objects travelling with uniform motion (constant velocity). the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. For example, a particle with. if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec.
From www.animalia-life.club
Zero Acceleration Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. For example, a particle with. the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. . Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT MOTION Describing and Measuring Motion PowerPoint Presentation Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration newton's first law can be used to explain the movement of objects travelling with uniform motion (constant velocity). the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity,. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From byjus.com
Which of the following four statements is false? (1) A body can have Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. For example, a particle with. if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4177184 Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec. to. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From brainly.in
an object can have zero velocity but constant acceleration? Justify Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration For example, a particle with. if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. newton's first law can be used to explain. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Usain Bolt is the world’s fastest man!!! PowerPoint Presentation Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration newton's first law can be used to explain the movement of objects travelling with uniform motion (constant velocity). if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. the equation ˉv = v0 + v. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From exocuphye.blob.core.windows.net
Constant Speed How To Find at Fidel Benson blog Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. newton's first law can be used to explain the movement of objects travelling with uniform motion (constant velocity). zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Kinematics equations for motion with constant acceleration Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration For example, a particle with. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. if the acceleration is. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From byjus.com
Sketch the displacement time, velocity time, and acceleration time Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec. For example, a particle with. if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.slideshare.net
Motion in one direction Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.animalia-life.club
Zero Acceleration Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec. zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Question 11 When an object is moving in a circle at constant Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration For example, a particle with. the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. . Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From slideplayer.com
VelocityTime Graphs What is it and how do I read one? ppt download Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. newton's first law can be used to explain the movement of objects travelling with uniform motion (constant velocity). if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Velocity and Acceleration PowerPoint Presentation, free download Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec. For example, a particle with. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From byjus.com
The position, velocity and acceleration of a particle moving with Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration newton's first law can be used to explain the movement of objects travelling with uniform motion (constant velocity). if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec. zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity,. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Changes in speed PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3685131 Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration For example, a particle with. if the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity (v = v 0), as expected (in other words, velocity is. the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. . Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.animalia-life.club
Zero Acceleration Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration zero acceleration can be a constant acceleration. For example, a particle with. if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec. the equation ˉv = v0 + v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant, v is just the simple average of the initial. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.
From www.youtube.com
How to Calculate Acceleration From a Velocity Time Graph Tutorial YouTube Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration if initial velocity is 5 m/sec and acceleration is zero, then the body moves with a constant velocity 5 m/sec. For example, a particle with. to newton, “uniform motion in a straight line” meant constant velocity, which includes the case of zero velocity, or rest. newton's first law can be used to explain the movement of objects. Is Constant Velocity Zero Acceleration.